How AI crawlers and bots read your site differently from humans (and why it matters)
AI crawlers and bots are now a second audience for your website, just as important as human visitors. When the vast majority of users use some type of generative AI-based chat or app to find information, especially when using the free tools, these AI apps don't actually "read" your website in real-time. What they do is either rely on their LLM's knowledge to return an answer, or they utilize existing search engine indexing to understand web sources.
So in this sense, how well your brand or product is represented in AI Search is a matter of:
A) How well the LLM's training data has absorbed information about you from your websites, other websites, social media, etc.
B) How well your website is being indexed in the various search engines that different AI engines use. For example Gemini naturally uses Google's indexing and ChatGPT uses Bing.
So when someone says "it's just SEO" they're partly right. Without well functioning SEO foundations, your website and brand have weaker chances of being part of the training process of LLMs, and also how well the search engines have indexed your content has a direct effect on the LLM's answers when they conduct "searches."
In this article you will learn:
- How AI crawlers and bots actually access and interpret your pages compared to human users
- The three layers of AI Search, from slow training data to real time agentic tools
- Which AI user agents you should usually welcome in 2026, and what they do
- Why bot traffic is becoming a leading indicator for future AI visibility
- Practical steps to prepare your site so both humans and AI agents can use it effectively
Once you understand how the machines see your site, it becomes much easier to debug visibility issues, protect your brand in AI answers, and use GEO analytics to guide your next optimizations.
What is actually different about AI Search compared to classic SEO?
AI search uses the same indexing foundations as SEO, but shifts the decision making from the user to the LLM, which breaks the classic “click into websites” funnel. LLMs haven't rewritten the rules of how websites are built or how indexing works, but they've created a new intelligent layer on top of it. The real difference is that it used to be the human user who at least to some extent decided the keywords and conducted to-the-point searches. Google and other search engines returned links that the user needed to click and scrutinize in order to validate whether the source was valuable. Now the LLM does this and provides the answers, often leading to so-called "zero-click" experiences as the scrutiny has already been done and content summarized in the AI's response.
So the real struggle for marketers isn't the "is it SEO?" question but rather the issue that the traditional performance funnel gets broken and the user experience is now different. If attribution was ever correct, now it's even more inaccurate. In AI Search, we don't have control anymore over the user's actions or the "funnel." That's why marketers are moving to adopt visibility metrics regarding their position in the conversations and using this as a critical KPI when measuring the success of their marketing and brand.
What are the three layers of AI Search and how fast are they?
AI Search can potentially produce faster results than traditional SEO but the reality is of course nuanced. AI Search operates on three distinct layers, each with its own speed dynamics:
Layer 1: Training data (the slowest layer)
This is where LLMs learn about your brand during their training process. It's the slowest layer, but not as slow as you might think. Based on Superlines research, we're seeing bots visiting sites almost every other day, suggesting they might be fine-tuning parts of their models quite rapidly. Still, getting into the base training data of major LLMs can take months.
Layer 2: High-volume AI Search (speed depends on your SEO)
This includes free ChatGPT, Google's AI Overviews, and similar tools or interfaces that rely heavily on existing search engine indexes. Here's the key insight: this layer is only as fast as your SEO is good.
If you have strong domain authority and consistently publish quality content, your visibility can improve rapidly. Potentially faster than traditional SEO because AI engines can surface your content in synthesized answers immediately after indexing. If your SEO fundamentals are weak, this layer can be just as slow as traditional search optimization. The speed advantage comes from understanding the connection between prompts, query fan-outs, and how your content addresses both.
Layer 3: Agentic AI (real-time & lightning fast)
This is where things get really interesting. Pro and advanced tools like Perplexity Pro, ChatGPT's Research and Shopping Assistant, and Claude Desktop with MCPs (Model Context Protocols) actually scrape and read your pages in real-time. These agents are intelligent, autonomous, and fast. Usage is growing rapidly, and this is where we're heading into true "agentic shopping" territory.
To summarize: AI Search isn't inherently faster than SEO but it's built on top of SEO infrastructure for high-volume queries. The speed advantage exists primarily in Layer 3 (agentic tools) and potentially in Layer 2 if your SEO is already strong.
How do LLMs take control over search queries
So even though the majority of LLM search uses SEO techniques, there's something completely different here. And here we're dipping our toes into the world where LLMs take "agency." It's not actually the user anymore who decides what the actual search queries are that are used to search the indexes but it's the LLM. They understand the users' questions or "prompts" and are able to break them down into multiple fan-out queries that fetch information from the indexed web content. So they add intelligence and have their own way of breaking the prompt into search queries.
This changes the whole game in performance marketing. Now besides impressions → clicks → web behavior → conversion, marketers need to understand the correlation between their position in the AI responses and their position in query fan-out results.
Why do AI Search results change so fast
Just like in SEO, all the different LLM providers are changing their algorithms and tuning their approach in how they switch between models, use search, or recommend brands. For example on November 24th, 2025, ChatGPT announced their Shopping Research feature, and around that time, brand visibility patterns started shifting, especially in certain industries (based on Superlines research and client experiences). So just like in SEO, marketers need to be constantly aware of the latest changes in the environment (meaning the algorithms or competitors smartly utilizing these new channels).
According to Cloudflare's 2025 analysis, AI and search crawler traffic grew by 18% from May 2024 to May 2025, with GPTBot jumping from #9 to #3 in crawler rankings and showing a 305% growth in requests.
What is the role of agents in AI Search?
The game gets interesting when we step away from the free AI tools or Google's Search AI mode / AI Overview, and break down how "pro" apps or features like "Research" in ChatGPT actually automatically, or based on user request, read and analyze your website. These more intelligent processes built natively to apps, built by users with n8n or connected MCPs, use LLMs in chains and usually various tools such as web scraping to actually read your website.
These so-called "user agents" have been around for a long time, but now LLM apps make them more intelligent and give them actual autonomy. Compared to how difficult it has been for marketers trying to guess each visitor's intent and finding the most profitable segments without violating anyone's privacy, this "agentic shopping" should be a fresh breeze, as many of the modern crawlers actually mean business:
"Hey, I'm here to audit your privacy!"
"Hey, I'm here to evaluate your pricing!"
"Hey, I'm here to read your product information!"
Who wouldn't want this in the marketing department? Instead of serving busy and confused humans, many agents are here for the business and they mean it (of course we have to also deal with spam and all kinds of miscellaneous crawlers).
In AI Search it's common to see a situation where the actual traffic from ChatGPT represents 1% of website traffic, but the bot traffic is already 20%. This indicates that the user experience is happening in the chat, and the user will find their way to your website from another route.
Now the big question is: how ready are companies, technically and mentally, to welcome the machines as customers?
Which AI user agents should marketers welcome in 2026
How many of you know, for example, that in Schema.org there are Action nodes that will help these little busy bees find the information and make moves? These structured data elements allow AI agents to understand not just what content is on your page, but what actions can be taken—from searching to purchasing.
Here's a breakdown of the most important AI user agents that marketers should welcome in 2026:
Source: Compiled from Momentic, Botify, and Cloudflare research
Important note: Some agents like "ChatGPT Atlas" and "OpenAI Operator" use standard Chrome user agent strings, making them indistinguishable from regular browser traffic (a challenge for those trying to monitor AI agent activity).
How can companies prepare for the agentic era
As Microsoft's NLWeb project demonstrates, the web's purpose is shifting from a link graph to a queryable knowledge graph. Here's what you need to do:
1. Implement Schema.org Markup
Use JSON-LD format to add structured data to your pages. Tip 1: focus on Action schemas that tell AI agents what they can do on your site (search, purchase, book, subscribe, etc.). Tip 2: Use tools like Superlines to optimize your schemas to match your business, target group and brand.
2. Optimize Your robots.txt
Make intentional decisions about which AI crawlers to welcome. Use tools like Knowatoa AI Search Console to test your robots.txt against 24+ different AI crawlers.
3. Monitor Bot Traffic
Check your server logs regularly to understand which AI agents are visiting and how often. Tools like Superlines can help you detect bot traffic but also connect the dots to prompt and query fan-out performance giving marketing and web teams accurate data to start serving the machines better
4. Structure Product Data
For e-commerce, ensure accurate pricing, specifications, availability, and reviews are available in structured formats. According to research on ChatGPT Shopping, source authority and structured data quality directly impact product recommendations.
5. Build Strong SEO Foundations First
Don't fall for the myth that AI Search replaces SEO. For high-volume AI Search (Layer 2), your visibility is directly tied to your SEO strength. Strong domain authority, consistent quality content, and proper indexing will make your content surface faster in AI responses.
6. Prepare for Real-Time Agentic Interactions
As Layer 3 grows, ensure your site can handle increased bot traffic and that your content is structured for intelligent agents to parse quickly. This includes clear heading hierarchies, semantic HTML, and machine-readable formats.
The agentic web is already here, but it's built on the foundation of traditional web technologies. Companies that understand how to optimize across all three layers (training data, indexed search, and real-time agents) will win.
See how AI bots actually read your site with Superlines Crawler Analytics
Most of this article has focused on what AI bots do in theory. The next step is seeing what they do on your own site in practice.
To really understand AI visibility, you need to see which bots visit your site, which pages they read and how that changes over time. Only then can you connect AI Search visibility, SEO work and content changes to real crawler behavior instead of guessing.
Superlines Crawler Analytics gives you a live view of your AI Search funnel, from the prompts and query fan outs that matter to the crawlers that actually read your content. You can see which LLM agents visit, which pages they care about and how that changes over time.
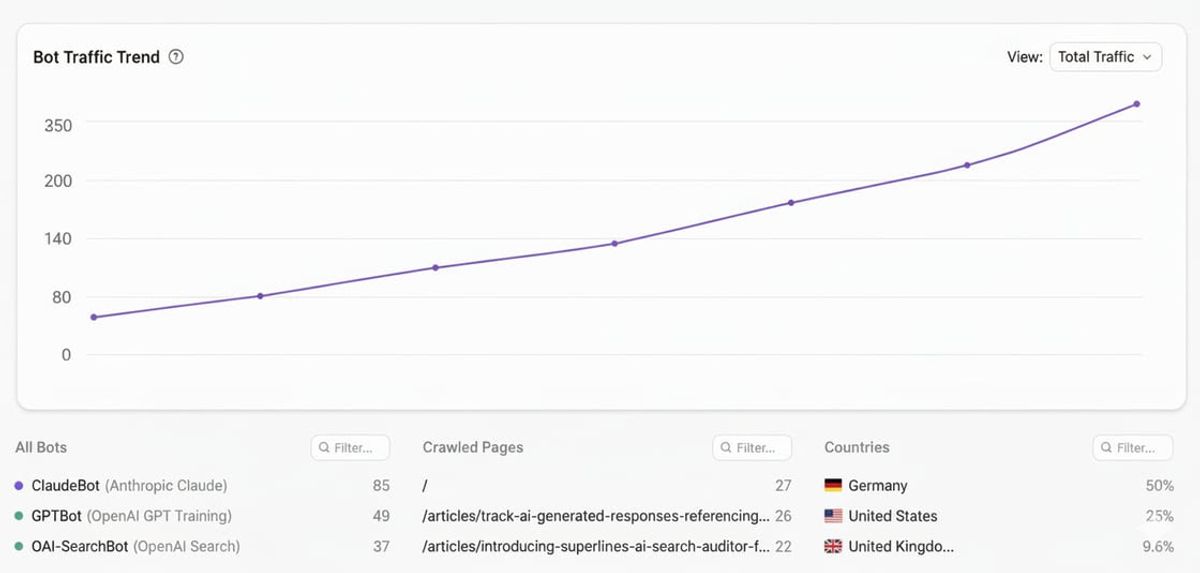
Once you know how bots read your site, you can finally connect AI visibility, SEO and content changes to real crawler behavior, instead of guessing.
